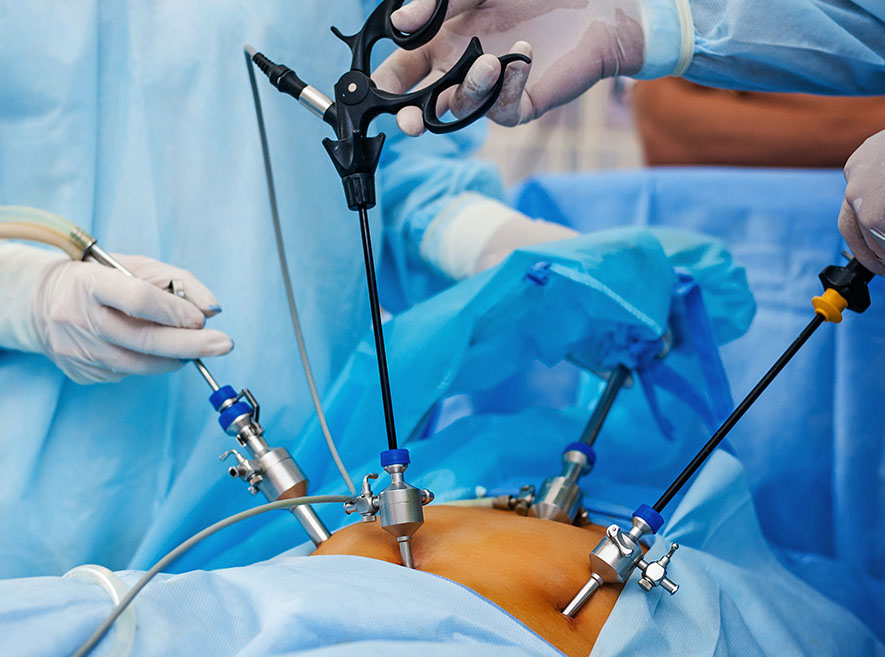
The most effective surgical alternative method to open or traditional gynecologic surgery is laparoscopic gynecologic surgery. It treats all types of gynecologic diseases using a minimally invasive technique. Laparoscopic gynecologic surgery requires only small incisions, whereas open gynecologic surgery necessitates extensive tissue cutting.
A laparoscope is used to examine the abdominal organs during laparoscopy. It is a thin, lighted tube that is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen. When a laparoscopic surgeon performs surgery the laparoscope’s camera sends images to a video monitor as it moves. It helps doctors to see inside pelvic organs such as the fallopian tubes, uterus, and ovaries.
Laparoscopic surgery is performed to identify and diagnose the source of pelvic or abdominal pain. There are a lot of cases where abdominal pain problem is diagnosed with imaging techniques such as Ultrasound, CT Scan, X-Ray, and MRI Scan. When these tests do not provide adequate information, laparoscopy is performed. Laparoscopy can also be done to take a biopsy or to take a sample of tissue from a particular organ in the abdomen.
Before undergoing laparoscopic gynaecological surgery, no special preparation is required. General anaesthesia is always used before surgery. It is always advisable to follow the surgeon's recommendations or instructions. First and foremost, a laparoscopic surgeon instructs the patient to sleep. A small needle is used to inject carbon dioxide gas into the abdomen. This gas keeps the abdominal wall away from the organs, lowering the risk of injury. The laparoscopic surgeon then makes a small incision in the abdomen. Through this small incision, the laparoscope is inserted. On a TV monitor, the camera displays images of the inside of the body. Images on a screen depict the pelvic organs, allowing the gynaecology surgeon to see and operate on them. Finally, the laparoscopic surgeon performs surgery in accordance with the type of gynaecological disease. When the procedure is finished, the surgeon removes all of the instruments and closes the incisions. The patient is then kept under observation to monitor any side effects and his or her recovery. He/she may experience pain or irritation in the treatment area, but serious complications are uncommon. Patients can sometimes go home the same day, but some complex laparoscopic surgeries require an overnight stay.